Loading...
Allergic rhinitis

Several allergy medications can improve symptoms and help you live with hay fever. These treatments come in many forms, including liquids, pills, eye drops, nasal sprays and injections.
You can take antihistamines to treat allergies. They work by stopping your body from making histamine.You can use decongestants over a short period, usually no longer than three days, to relieve a stuffy nose and sinus pressure.
Asthma
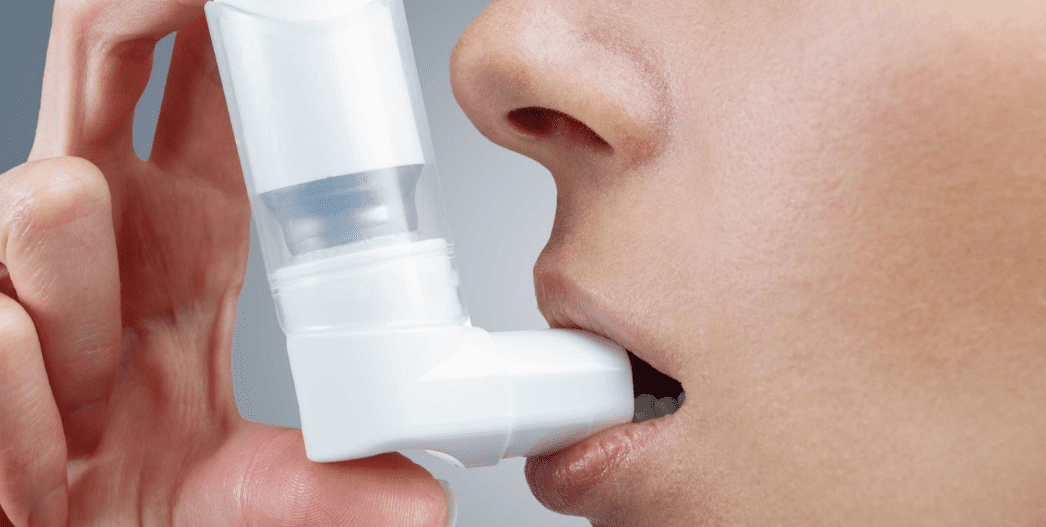
You have options to help manage your asthma.These include:
- Bronchodilators: These medicines relax the muscles around your airways. The relaxed muscles let the airways move air. They also let mucus move more easily through the airways. These medicines relieve your symptoms when they happen and are used for intermittent and chronic asthma.
- Anti-inflammatory medicines: These medicines reduce swelling and mucus production in your airways. They make it easier for air to enter and exit your lungs. Your healthcare provider may prescribe them to take every day to control or prevent your symptoms of chronic asthma.
- Biologic therapies for asthma: These are used for severe asthma when symptoms persist despite proper inhaler therapy.
Dust mite, pollen, fungal allergies

Antihistamines relieve itching, sneezing, and watery eyes.
Decongestants ease or unclog a stuffy nose.
Nasal steroids reduce swelling in your nose so you can breathe better.
Leukotriene modifiers block certain chemicals in your immune system.
Other treatments include:
Allergy shots (immunotherapy) to train your immune system not to react
An allergen extract (Odactra) under the tongue, which can replace shots
Nasal irrigation with a saline solution, which can clear out your nose and sinuses
Breathing difficulties

Treatments for breathlessness include:
- Inhaled medications that help open the airways
- Drugs to treat specific conditions
- Pills or liquids to help reduce sputum and clear the lungs
- Drugs to manage allergies
- Treatment for a heart condition
Food allergies
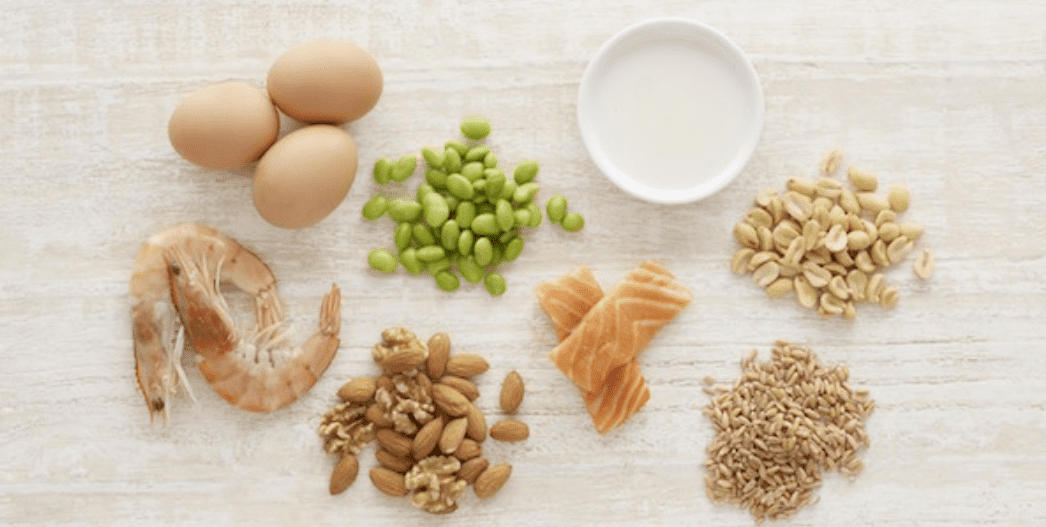

When you know what foods you are allergic to, the best approach is to strictly eliminate those foods from your diet and to have emergency medications including epinephrine autoinjectors available at all times in case of accidental ingestion and reaction. It’s important to seek emergency medical care immediately after using an epinephrine autoinjector. Wearing a medical alert identification indicating your food allergies is also recommended.
Allergic urticaria
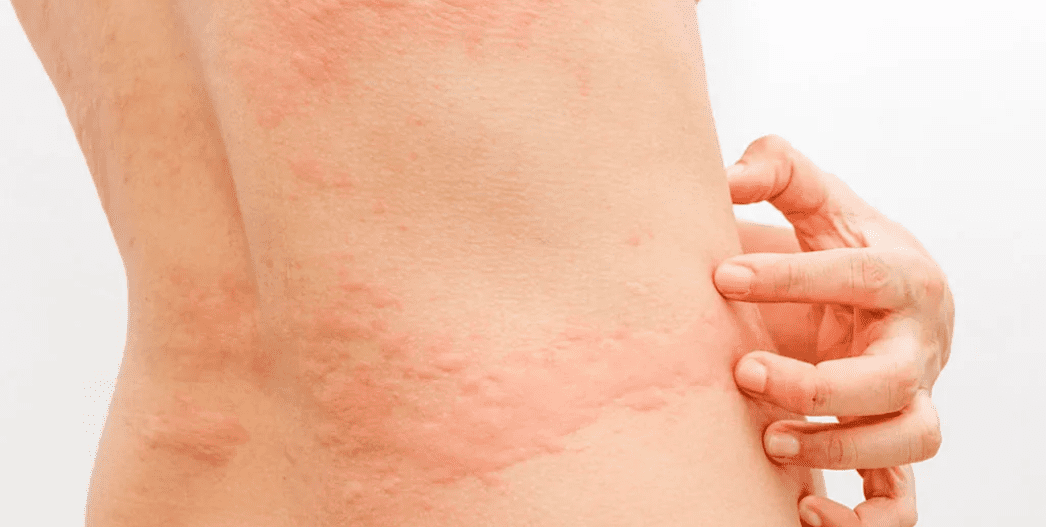
Treatments for allergic urticaria may include prescription drugs:
- Anti-itch drugs: The standard treatment for hives and angioedema is antihistamines that don't make you drowsy. These medications reduce itching, swelling and other allergy symptoms. They're available in nonprescription and prescription formulations.
- Drugs that suppress the immune system: If antihistamines are not effective, your doctor might prescribe a drug that can calm an overactive immune system.
- Drugs for hereditary angioedema:If you have the type of angioedema that runs in families, you may take medication to relieve symptoms and keep the levels of certain proteins in your blood at levels that do not cause symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: For severe hives or angioedema, doctors may prescribe a short course of an oral corticosteroid drug — such as prednisone — to reduce swelling, inflammation and itching.
Drug allergies

The following interventions may be used to treat an allergic reaction to a drug:
- Withdrawal of the drug: If your doctor determines that you have a drug allergy — or likely allergy — discontinuing the drug is the first step in treatment. In many cases, this may be the only intervention necessary.
- Antihistamines: Your doctor may prescribe an antihistamine or recommend an over-the-counter antihistamine such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) that can block immune system chemicals activated during an allergic reaction.
- Corticosteroids: Either oral or injected corticosteroids may be used to treat inflammation associated with more-serious reactions.
- Treatment of anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis requires an immediate epinephrine injection as well as hospital care to maintain blood pressure and support breathing.
Skin allergies
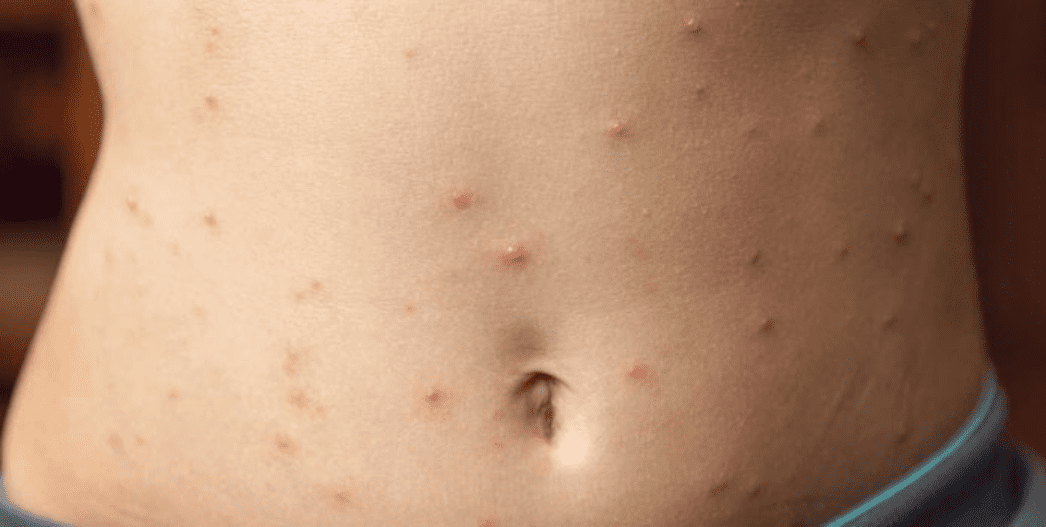
The best method is prevention. Find out what causes your rash and avoid it. You may need to wear gloves to protect your skin.
When you do have a reaction, try to ease the symptoms and prevent an infection. Don't scratch, even though that's a hard urge to resist.
Over-the-counter products and home remedies can help relieve the itching and stop the swelling. Try these:
- Hydrocortisone cream
- Ointments like calamine lotion
- Antihistamines
- Antihistamines
- Oatmeal baths